Comparing Optimization Algorithm Choices in ADMM
Akarsh Goyal
2020-08-31
compare_opt_algo.RmdThis tutorial shows how to compare perfomance of ADDM solver for different optimization algorithm choices. In this example, we will compare Newton-Raphson method, BFGS method and L-BFGS method.
# Generating data n <- 1000 p <- 40 d <- randomProblem(n, p, response = "binomial", density=0.5) x <- d$x y <- d$y
Now that we have out training data-set, we will use ADMM to obtain the fit thrice - once with Newton-Raphson as optimization algorithm, once with BFGS as optimization algorithm and finally once with L-BFGS as optimization algorithm. Note that diagnostics=TRUE flag is necessary so that solver records the metrics at each iteration.
# Obtaining the fit for the solvers we want to compare admm_nr <- ADMM(x, y, family="binomial", opt_algo="nr", alpha=(0.01),diagnostics=TRUE) admm_bfgs <- ADMM(x, y, family="binomial", opt_algo="bfgs", alpha=(0.01),diagnostics=TRUE) admm_lbfgs <- ADMM(x, y, family="binomial", opt_algo="lbfgs", alpha=(0.01),diagnostics=TRUE)
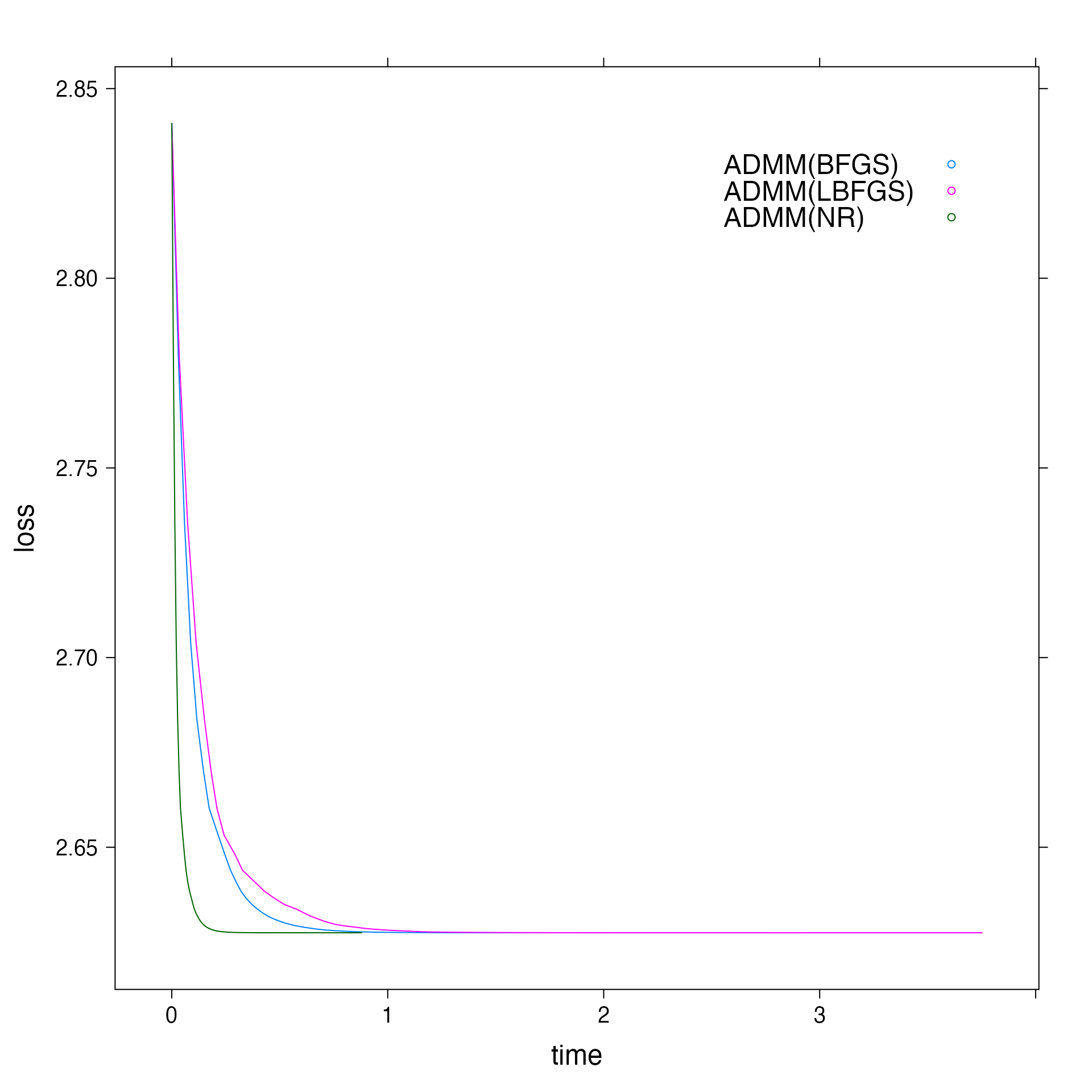
To compare total execution time, we can use total_time attribute of the fit.
# Comparing total execution time print(admm_nr$total_time) #> [1] 0.8868921 print(admm_bfgs$total_time) #> [1] 2.945276 print(admm_lbfgs$total_time) #> [1] 3.778316
Now, these fits cannot be directly used to plot as they contain a lot of parameter so we’ll call a utility function that merges the relevant parameter and returns a dataframe.
Finally, now we can generate the loss vs time plot.
# Plotting objective vs time plt <- xyplot(loss ~ time, group = solver, data = f, auto.key = list(corner = c(0.9, 0.9)), type = "l") update(plt, par.settings = list(fontsize = list(text = 18)))